|
Published results: (older
results) |
|
 |
Fractionalized modes: The Kiteav model with
anisotropic exchange on a honeycomb-like lattice predicts
the existence of topological excitations with fractionalized
quantum statistics. Such modes have recently been predicted
and now observed experimentally in quasi-3D coordinated
Iridium oxides, see
Nature Commun., in print (2016). |
|
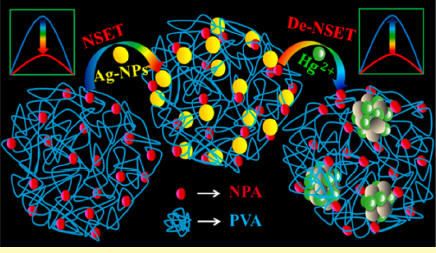 |
Mercury a serious health
thread ... can be
detected using Ag nanoparticles with a turn on
ultrasensitive fluorescence sensor and a linear regime from
0 to 1 ppb, P. K. Sarkar, et al.,
ACS Sensors (2016). |
|
 |
Plexcitons in a periodic
structure... periodic
arrays of plasmonic Au wires in proximity to a dye shows
strong coupling to molecular excitons. Such plexcitons can
be modelled in some microscopic approach using a Zubarev
Green's function method following the work of Manjavacas et
al.., preprint by Liu Bo, et al. (2016). |
|
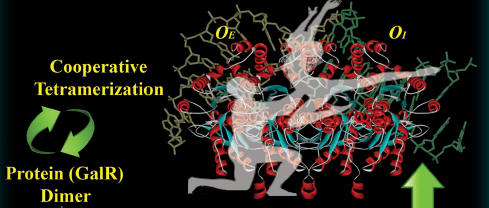 |
The Dance of DNA... Although many
forms of dynamical behaviour of proteins under allosteric
interactions with effectors are predicted, little evidence
of dynamics in the interaction has been reported. Here, we
demonstrate the ultrafast dynamics of the allosteric
interaction of the Gal repressor (GalR) protein dimer with
DNA operator sequences using time resolved optics , see S.
Choudhury, et al.
ChemBioChem (2016) |
|
 |
Editors Choice... Evidence for a
Z2 quantum phase transition from a dimer to a resonating
valence bond state driven by singlet fluctuations. The rich
spectrum of singlet bound modes is attributed to a melting
of a dimer crystal, see
Phys. Rev. Lett. 110 (2013). |
|
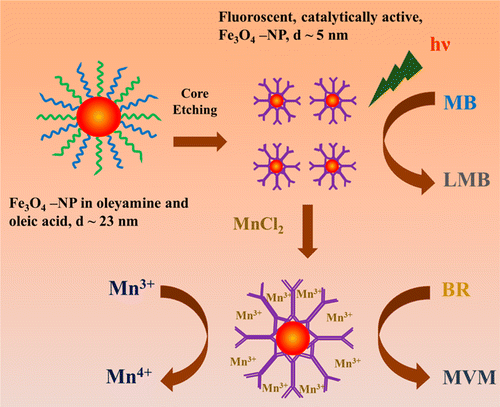 |
Surface engineering of various nanoparticles (NPs) is of growing interest and an important
step to induce/control optical and/or catalytic activities. Here we report a top-down fabrication methodology to
modify a model ferrofluid with parent NPs sizes of about 23 nm. The surface engineering involves ligand exchange
and simultaneous phase transfer, and core etching, resulting in a reduction of particle diameter to
about 5 nm. We have used the functionalized NPs for the photodegradation of biomedically important jaundice marker
bilirubin in aqueous solution. Overall, the results represent a promising route for the fabrication of NPs
adaptable to diverse applications, see
Journ. of Phys. Chem. C (2014). |
|
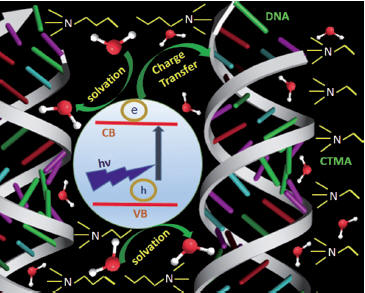 |
Charge migration along DNA molecules is a key factor for
DNA-based devices in optoelectronics and biotechnology.
We have investigated the role
of water molecules in DNA-based
materials for the intactness of the DNA structure and
their dynamic role in the charge-transfer (CT) dynamics.
This study uses time resolved optical spectroscopy and is
based on a collaboration between groups from Kolkata, Idia
and the TU-Braunschweig,
see
Chemistry, An Asian Journal (2014). |
|
 |
In the giant Rashba
system BiTeI as well as in topological insulator there exist
an enhanced
quasiparticle dynamics of quantum well states.
This is due to a time dependent band beneding leading to a
surface confined quantum well state. Topological insulators
and Giant Rashba system share a very similar surface
chemistry and strong spin orbit coupling of bulk and surface
states. However, they have a different symmetry in the bulk.
This leads to a different symmetry of electronic Raman
scattering, see
PRB. |
|
 |
A novel solid
solution (Co1-xNix)3Sb4O6F6
with a pseudo
kagome structure can be taylored with
respect to its physical properties by changing its
composition. This systems can be used to better understand
the interplay of dimensionality, anisotroy
and magnetism within one crystallographic structure.
This is a collaboration between groups from Stockholm,
Houston and Braunschweig,
see
Chem. of Mat., (2014). |
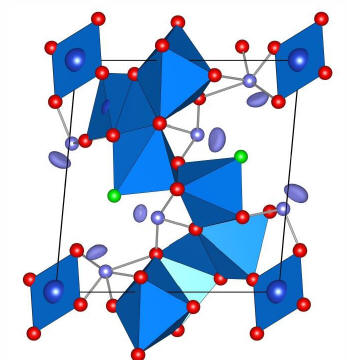 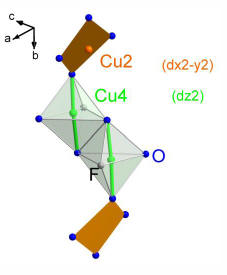 |
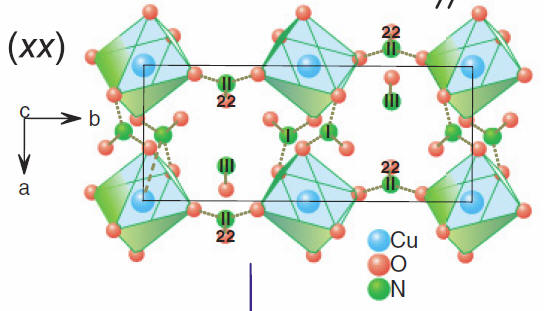
The novel oxofluoride
Cu7(TeO3)6F2
shows features of
both zero and one dimensional magnetism.
This is due to an interplay of composition that contains
fluorine ions as well as the lone pair element Te with the
electronic configuration of the Cu 3d
orbitals.
In contrast to many other compounds the fluorine terminates
the magnetic exchange path. Te with its lone pair electrons
opens up the structure like a scissor. The alternation of
different Cu orbitals (see right figure) has a further
important consequence for the exchange from one Cu2 sites
(brown plaquette) to the other. As a result low energy
fluctuations exist in a broad temperature range. This is a
collaboration between groups from Stockholm, Houston and
Braunschweig, see
Inorganic
Chemistry, (2014). |
 |
Dynamic lattice distortion and spin
fluctuation cooperate in the spin liquid phase of a
low-dimensional compound nitrosonium nitratocuprate.
This system has been proposed to be a model compound for the
resonanting valence
bond ground state (RVB).
Our data, however, point towards a structural instability at
low temperatures that freezes out spin correlations by an
excitation gap
(Phys. Rev. B 85, (2012)
and
cond-mat). |
|
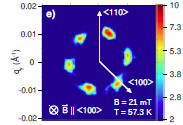 |
The magnetoelectric compound
Cu2OSeO3
shows a state with an inhomogenous spin polarization called
SKYRMION phase. These objects are
topologically protected and form a
superstructure that can be investigated by small angle
neutron scattering. The skyrmion phase in an insulator with
coupled dielectric-spin degrees of freedom allows new
applications in the field of spintronics
(Phys.
Rev. Lett). |
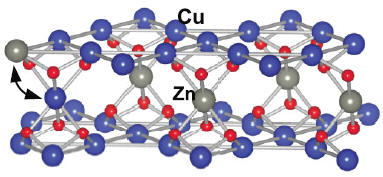 |
Frustrated quantum spins realized by
transition metal ions in solids form states of matter with
novel properties. We show how a modification of the chemical
composition in zinc paratacamite can be used to tailor its
magnetic properties from a spin liquid to a spin glas
(Phys.
Rev. B
and
cond-mat). |
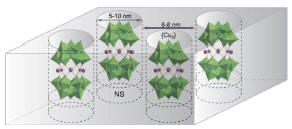 |
Molecules that consist of
three Cu ions and are arranged in
a lattice (freestanding porous silicon) realize a novel
hybrid material. It
provides a promising scheme for implementing spin-based
quantum gates. By measuring the spin relaxation times of
samples with different symmetries and
environments we give evidence that a spin chirality is the
main decoherence source of spin triangle
molecules (Phys.
Rev. Lett.).
|
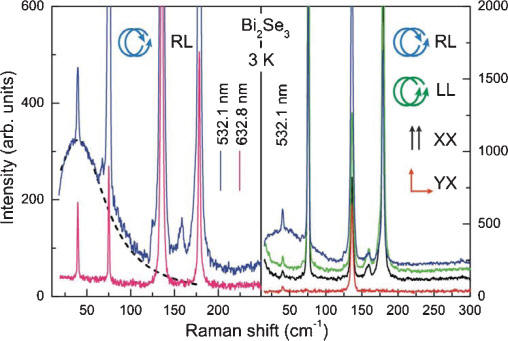 |
Topological insulators allow collision
dominated scattering with spin-helical symmetry. This
scattering is due to fluctuations from Dirac to bulk states
of the compound despite topological protection. The
scattering rate is determined from the position of a maximum
in the RL scattering component as
G=40cm-1
(Phys.
Rev. B). |
|

|
Magnetic
molecules can be tuned by a confinement in the nanocage of a Protein,
(Chem
Phys Chem). |